- Article
Rheological and Thermal Properties of Recycled Petroleum-Based Polyesters MWCNT Nanocomposite: Sustainable Materials
- Kashif Ullah Khan,
- Zoltan Weltsch and
- Andrea Adamne Major
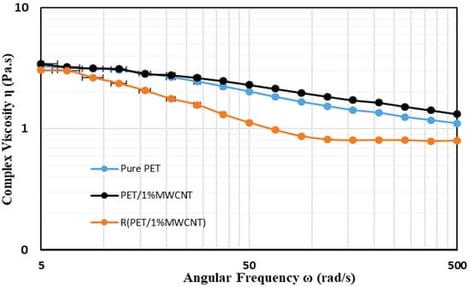
This work investigates the effect of recycling on the rheological and thermal properties of petroleum-based polyester nanocomposites. PET and PBT are used widely in the automobile and packaging industries, and there is a growing need for effective ways to utilize recycled polyesters. The melt mixing method was used to prepare the nanocomposites using a twin-screw extruder. After recycling, the rheological properties of the PBT nanocomposite remained stable, as the degradation of PBT chain was low due to the presence of MWCNT and molecular chain flexibility. In contrast, the complex viscosity of PET recycled nanocomposite decreases significantly because the high processing temperature of 280 °C led to substantial polymer chain scission and network breakdown. Due to the presence of MWCNT, PET and PBT nanocomposites show higher thermal stability than pure and recycled nanocomposites. The recycling of PET and PBT nanocomposites demonstrated potent thermal stability under inert and air/oxidative atmospheres. These results indicate that the effect of recycling strongly depends on the polymer matrix: while PET-based nanocomposites exhibit notable reductions in rheological properties after recycling, PBT-based nanocomposites retain stable rheological and thermal performance due to MWCNT reinforcement. The enhancement in this research could make the recycled materials valuable for the automotive industry.
7 February 2026



![The comparison of SEA performances of several CFRP geometries [14].](https://mdpi-res.com/cdn-cgi/image/w=281,h=192/https://mdpi-res.com/jcs/jcs-10-00085/article_deploy/html/images/jcs-10-00085-g001-550.jpg)